
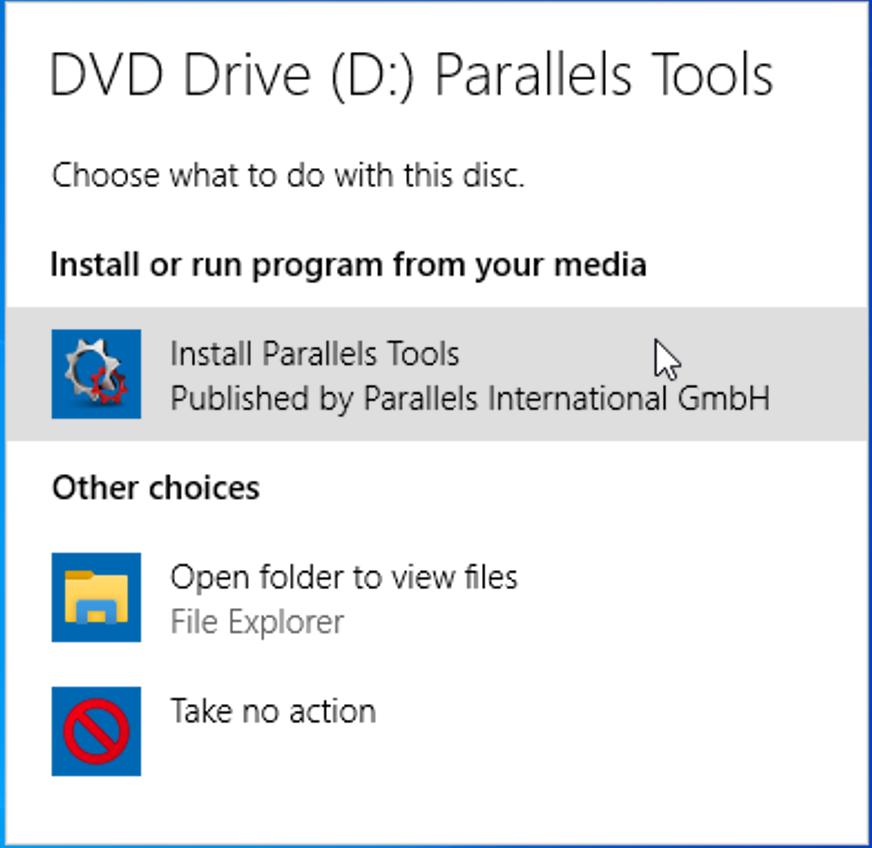
The delete doesn’t finish any faster.Īnyhoo, setting aside stunt examples, back to the problem itself. However, there’s no parallelism in the delete operation itself, just during the meaningless operation to “find” the rows that match, which is of course all of them. In that case, SQL Server uses parallelism to “seek” on an index, discovers that all rows match, and then sets about doing the delete. This query is single-threaded, but…could we get a parallel operator anywhere in the plan, and if so, will the query go faster? Well, we can kinda sorta gain parallelism by injecting a meaningless filter that matches all rows. Watching the live query plans with sp_BlitzWho, we can see SQL Server working through the plan, one index at a time, sorting millions of rows of data. The plan has no parallelism operators, which in turn heats up one CPU core, which then sets 148,723 query bucks on fire: This database is the starting point for the Mastering classes – I drop different indexes on it depending on which lab folks are doing – and it happens to nicely replicate the kind of problem the client faced. The execution plan isn’t pretty: What 148,723 Query Bucks looks likeįor this demo, I’m using the 40 million row, 105GB Posts table, and it’s got 13 indexes on it. Right now, all you’re doing is a simple delete:

Say you need to periodically erase the contents of a table and start over, and your app doesn’t have the permissions required to do a truncate table. I figured I should blog about this because I polled y’all on Twitter, and you weren’t sure about it either:ĭo DELETE queries go parallel in SQL Server? (Assume just one big table in the query, no joins, no subqueries.) Poll:Īnd there was even disagreement between those of y’all who WERE sure, hahaha, so let’s walk through it. To help tell the story, I’ve reconstructed versions of them with the large Stack Overflow database. I had to troubleshoot a couple of different slow deletes, and in both cases, parallelism questions came up.

Thank goodness I bookmarked it, because I moved on with my life and totally forgot about it until recently. Changes are applied serially to the database in these cases. But if the UPDATE or DELETE statements contain a WHERE clause, or an INSERT statement contains a SELECT clause, WHERE and SELECT can be executed in parallel. For example, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE are not normally processed in parallel even if the related query meets the criteria.
Years ago, when troubleshooting performance, I stumbled across this Microsoft documentation on parallel query processing that says:Ĭertain types of statements cannot be processed in parallel unless they contain clauses, however.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
